This page is part of archived documentation for openHAB 4.1. Go to the current stable version
# Blockly Reference
One of the core feature that openHAB provides is writing rules to allow specific behaviour with the home automation system. The usual way of developing rules is by coding them like described in the Textual Rules.
However, this art of programming may become intimidating early on and shy away away people with few or almost no experience in programming. Therefore openHAB also provides a graphical way of writing rules which allows to put together rules in a rather visual way (even though some programming background may still help).
# Introduction
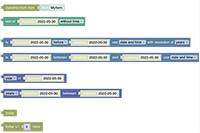
The basic idea behind the visual paradigm and representation within openHAB is based on the Google Blockly Support (opens new window) which has been integrated and which provides the basic blocks for programming like the ones on the left and the right side of the below images Blockly toolbox


All of these provide general functionality that is not specific to openHAB itself. If you want to learn more about how to use them, search for the many blockly tutorials that are available. However, to leverage the full capabilities more than 50 specific blocks have been provided that are tailored for easy access of openHAB's capabilities.
This section provides a detailed description of the specific blocks and provides examples on how to use them. Note that some of the blocks (like voice, streaming or notifications) need some special setup within openHAB - in these case links to the respective documentation is provided.
Also see this Intro (opens new window) Quick Intro Blockly Rules
# Blockly is a code generator or how the 🦏 found the holy Grail
# Some history
Even though you may not notice it directly, the blocks are eventually used to automatically create code that can run on the openHAB server.
Please watch the video Blockly as an ECMA-Script code generator (opens new window) for a live demo.
The code that is generated can be viewed when clicking the button
on the lower right corner of the blockly editor.
In general, the code that Blockly generates is JavaScript (aka ECMAScript) which exists in several flavours or versions. The ECMAScript version that is used by Blockly in openHAB 3 is ECMAScript 5.1 and it is run by a component named NashornJS 🦏. Nashorn JS (opens new window) itself was part of Java until version 14 when it was dropped. The generated rule code is run within the Java runtime (also known as JVM) on the openHAB server and as openHAB 4 has moved to Java 17, the old ECMAScript 5.1 is not directly available anymore within the JVM via Nashorn. A replacement for the Nashorn JS is GraalJS ("the holy grail"), which is currently running ECMAScript 2022 and therefore supports all modern JavaScript features, like arrow functions. GraalJS (opens new window) is already available in openHAB 3 when the JS Scripting Addon (opens new window) is installed.
TIP
Please convert your old rules as quickly as possible because only with GraalJS you can leverage the openHAB JavaScript library (aka openhab-js) in Blockly. Using this library you can not only create much simpler code, it also allows new functionality that is not available with Nashorn. Note that some blocks are only available with the openhab-js library on GraalJS.
# openHAB 3 / openHAB 4 - Migration
# Migrating Blockly rules to openHAB 4 is easy
From openHAB 4 on, the default script engine is GraalJS when Blockly creates new scripts.
From a technical perspective a rule internally holds a so-called MIME-type that tells openHAB how the generated JavaScript language has to be interpreted.
The (default) MIME-type application/javascript in openHAB 3 runs the rule with NashornJS, while this same MIME-type will run the Blocky rule with GraalJS in openHAB 4.
As a result when running a non-converted openHAB 3 Blocky rule on openHAB 4, openHAB 4 will run a rule that was meant for NashornJS with GraalJS, which will fail.
Therefore a conversion has to take place which in fact is not a lot of work:
There is the choice to
- convert each rule to GraalJS
- or keep the NashornJS Rules
but both need some work on each blockly rule you have.
# Migration to GraalJS (recommended)
- Make sure the JS Scripting Addon (opens new window) addon is installed.
- To convert / migrate a rule that was created in openHAB 3 (NashornJS) to a GraalJS-compatible one for openHAB 4, simply open each Blockly rule once in openHAB 4 and save it - that's it.
- In this case, nothing more needs to be installed additionally to openHAB 4.
# Running openHAB 3 Blockly rules without migrating them right away
- If you still want to run the Blockly rules that were created in openHAB 3 for the time being without changing them (see above), you have to install the JavaScript Scripting (Nashorn) Addon (opens new window) which provides backwards compatibility until you have converted all rules.
- Open each Blockly rule or go to the Code TAB or Search for type: application/javascript;
- Replace it by
application/javascript;version=ECMAScript-5.1. Open the Blockly rule, find the following symbol and click on it.
to choose the old version of JavaScript and then save the rule.
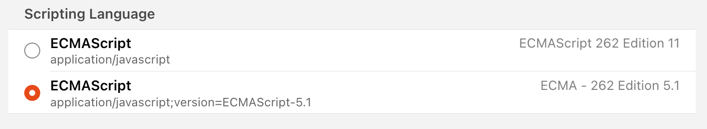
- After the installation of the Addon both old rules created in openHAB 3 and new rules created in openHAB 4 can run on openHAB 4 at the same time.
- After all scripts of the rules have been converted, like explained above, please uninstall the JavaScript Scripting (Nashorn) addon to save memory.
- Note that this allows you to mix rules that run with NashornJS and some that run with GraalJS (see above).
# Looking for help
A special mention should go towards the Help entry in a block context menu right click on any block that links to a resource that is usually very helpful to understand the context of that particular block. To retrieve the particular help for a block right click on a block to open the context menu and click on the help-entry:
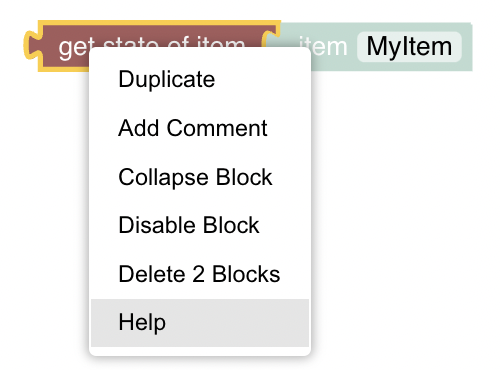
There is also a help-button available in each section that links to the documentation of the whole section.
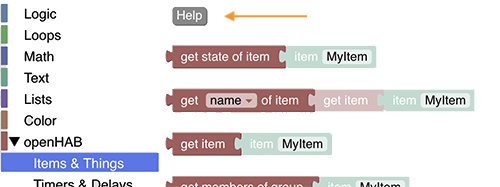
Please read this information first before asking questions in the forum. In case you ask for help please always post the respective code that is being generated.
Also there is a good intro about that topic can be viewed at Various Help Documentation available in openHAB Blocky (opens new window)
# Before using blockly
Please visit Getting started with openHAB Blocklies and creating a rule before asking questions in the forum.
# Blockly Youtube Tutorials
Three Youtube tutorials have been made available via the openHAB Youtube channel (opens new window):
- Episode 1 (opens new window)
- Introduction (opens new window)
- Quick Intro Blockly Rules (opens new window)
- Debugging Rules with openHAB Developer Tools to watch Item-Status (opens new window)
- Creating a Blockly Rule (opens new window)
- Overview of the Blockly Sections (opens new window)
- Logging (opens new window)
- Working with Items (opens new window)
- Working with Text-Blocks (opens new window)
- Sending Commands (opens new window)
- Using Color-Blocks and HSB-Conversion (opens new window)
- Waiting in Rules (opens new window)
- Various Help Documentation available in openHAB Blockly (opens new window)
- Blockly as an ECMA-Script code generator (opens new window)
- Loops in Blockly (opens new window)
- Playing sounds on audio sinks (opens new window)
- Using Text-to-speach easily with blocks (opens new window)
- Streaming Music (opens new window)
- Episode 2 (opens new window)
- Episode 3 (opens new window)
- Datetimes and Cron-Triggers (opens new window)
- Copy-Of, Datetime-Now with Math-Operations (opens new window)
- Datetime - Temporal Units (opens new window)
- Date comparison (opens new window)
- Creating Datetimes and other datetime blocks (opens new window)
- Convert item states to Datetimes (opens new window)
- Send Notifications to the openHAB mobile app (opens new window)
- Using Ephemeris information (opens new window)
- Using Persistence data (opens new window)
- Wrap up and short overview on basic blocks (opens new window)
- Basic: Logic, Loops, Variables overview (opens new window)
- Basic: Math (opens new window)
- Basic: Text (opens new window)
- Basic: Lists, Colors (opens new window)
- openHAB Blocks Wrap up (opens new window)
- Global Value Storage (opens new window)
- Run & Process blocks, transform (opens new window)
- Inline Scripts (opens new window)
- Outro (opens new window)
# Blocks Overview
Also view Overview of the Blockly Sections (opens new window)
# Items and Things
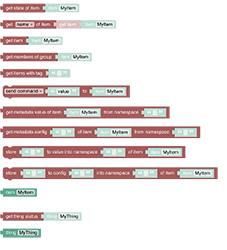
Items and Things are the major entities of openHAB (opens new window) to control and monitor the home.
See Items & Things section
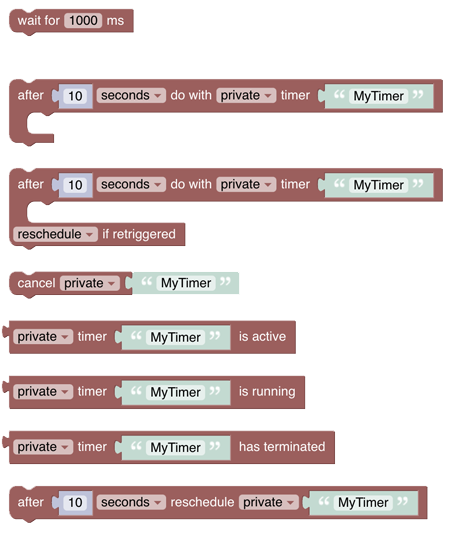
# Timers and Delays
Timers and Delays are a little more complex but add important functionality to rules. Whilst the “Wait-For”-block is straightforward, the timer blocks should be well understood before being used - they may behave differently than expected. This chapter explains what these blocks do, sometimes displaying generated code to explain what is happening behind the scenes.
See Timers and Delays section.
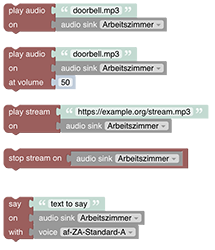
# Voice and Multimedia
This section deals with playing or streaming audio to an audio sink e.g a speaker or saying a text via using any Text-to-Speech API (e.g. Google's API)
See Voice and Multimedia section.
# Units of Measurements
See Units of Measurement section.
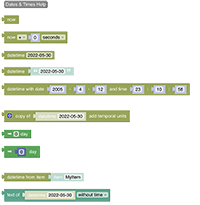
# Date Handling
Date blocks are used as input parameters for other blocks. Some of these blocks are used by ephemeris blocks, whilst others are used in the persistence section. Therefore blocks are typed to assure correct connection to other blocks.
See Date Handling section.
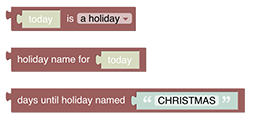
# Ephemeris
The ephemeris category provides blocks with calendar functionality. The blocks can be used to determine what type of day today is, or a number of days before or after today is. For example, a way to determine if today is a weekend, a bank holiday, someone’s birthday, trash day, etc.
See Ephemeris section.
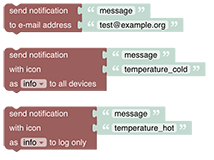
# Notifications
For use with your openHAB cloud (opens new window) account, these blocks can be used to send notifications to relevant connected devices. Notifications can be used as push message to devices running the openHAB client.
See Notifications section.
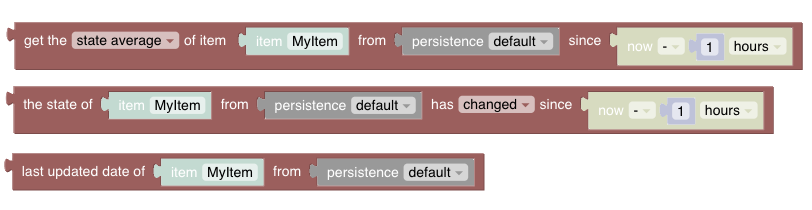
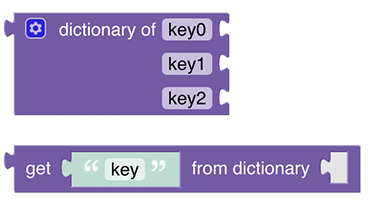
# Persistence
Persistence blocks enable access of historical data stored by the default persistence service.
See Persistence section.
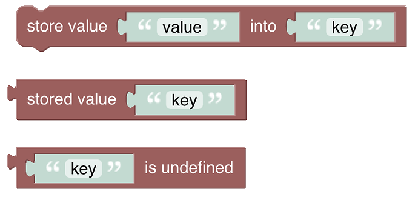
# Value Storage
These blocks enable storing information for a rule that is kept after the rule has run, so it can be reused when the rule is run again later in stateful way.
See Value Storage section.
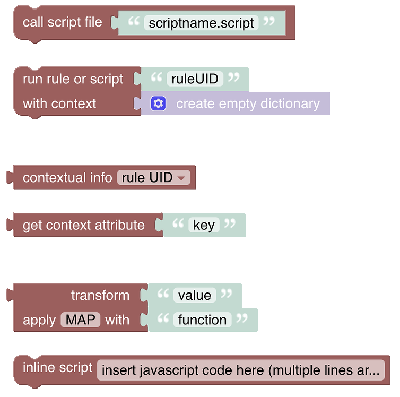
# Run & Process (Rules, Scripts and Transformations)
This section allows calling rules or other scripts, retrieving attributes provided by the rule context or transforming values via different conversion methods (e.g. map, regex, jsonpath)
See Run and Process section.
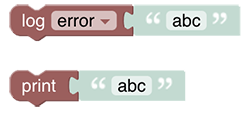
# Logging
This section allows calling rules or other scripts, retrieving attributes provided by the rule context or transforming values via different conversion methods (e.g. map, regex, jsonpath)
See Logging section.
# openHAB Extensions to the Standard
This section explains only the blocks that have been added to the standard blocks by openHAB
See openHAB Extensions to the standard section.
# openHAB Blocks provided by the community
The core openHAB are meant to cover most of the functionality that is needed to write rules. However, there might be functionality that is not available (yet). These can be provided by the community.
A good explanation on how to write custom blocks can be found at How to write openHAB Blockly Libraries (opens new window)
All published custom blocks can be found at Published Blockly Libraries (opens new window) and can be directly downloaded within your openHAB installation in the Settings -> Automation section
# Tutorials or other useful information
- Getting Started: Rules - Blockly (opens new window)
- Extending Blockly with new openHAB commands (opens new window)
← Rules Transformations →